The study of pedestrian dynamics and of the design of walking spaces plays a significant role. Lift offers a new service of simulating pedestrian flows and optimizing pedestrian facilities.
Nowadays pedestrian dynamics are increasing their importance. In line with the aim of improving citizens’ life quality in big developing cities, studying the best solution for more efficient transport terminals and infrastructural nodes is essential to enable people to move rapidly from one point of the city to another. So, the study of pedestrian dynamics and the design of walking spaces play a significant role. Lift may offer a new service of simulating pedestrian flows and optimizing pedestrian facilities.
An innovative methodology combining simulation and optimization has been successfully applied to some case studies obtaining promising results for the dimensioning of pedestrian facilities given specific requirements on their level of service.
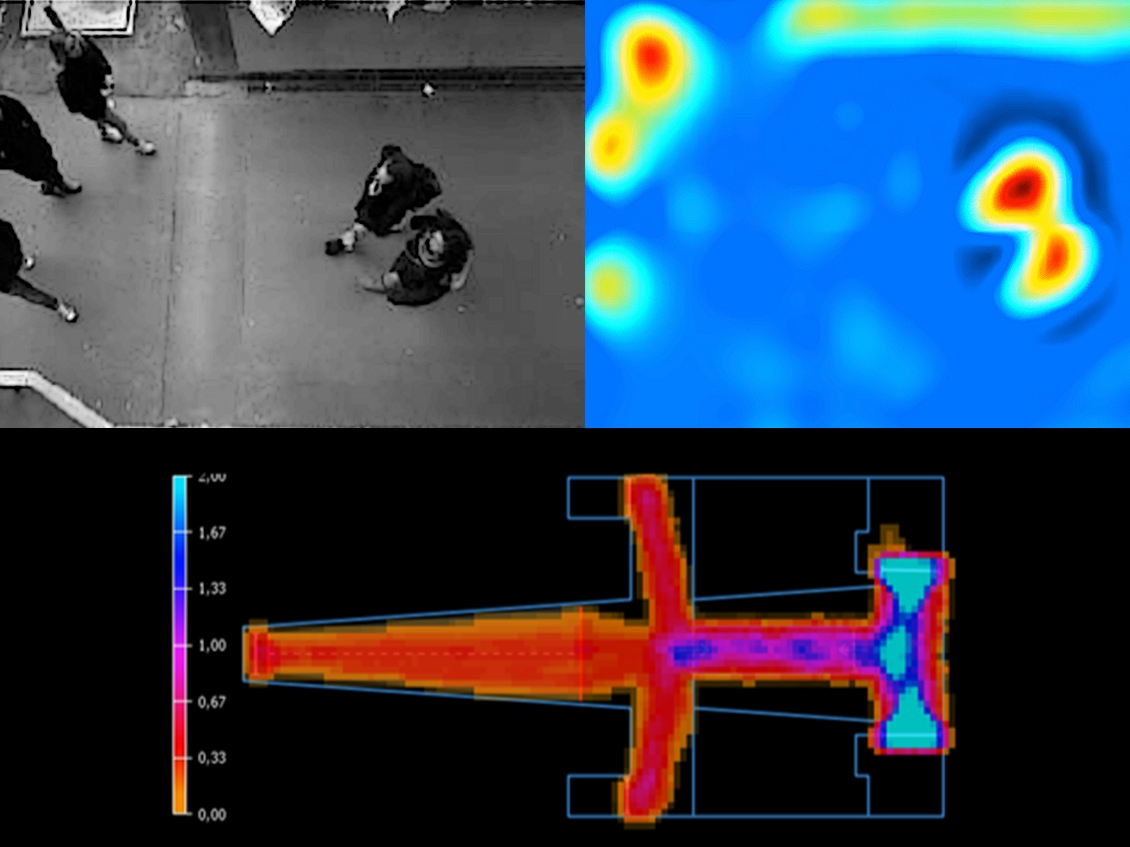
It allows pedestrian tracking inside buildings and the estimation of some parameters which are required for the calibration of microsimulation models.

Integrated planning of railway operations and station layout to improve pedestrian level of service (LOS). In railway and metro stations, pedestrian traffic volumes are certainly influenced by train arrival and departure timings, during which some peak flows can occur. In this context, together with a LOS analysis performed using static analytical methods, the proposed optimization approach has enabled to relate the presence of pedestrians and their corresponding traffic peaks to the train timetables, providing optimal solutions for the maximization of the number of users within the station while respecting the limitations due to social distancing. As for example, such approach has been adopted in two relevant nodes of the Italian railway network, namely at the Roma Termini station and on one of the platforms of the railway station connected to the Fiumicino Airport.
Selected References:
Roma Termini station
Fiumicino Airport

Lift Research and Development department developed a new analytical methodology for the estimation of pedestrian behaviour inside terminals.
Using a multi-fidelity approach and specific Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithms, Lift developed a methodology to optimize the most important dimensions of pedestrian facilities.
This approach has been tested in a number of METRO stations leading to an improvement of LOS without changing the area of pedestrian facilities
Selected References:
Dynamic supportive planning interface